
A Guide to Operationalizing NPC Data Privacy Compliance for Your Organization
Safeguarding personal data in the Philippines constitutes a statutory obligation, extending beyond standard best practices. The Data Privacy Act of 2012 established the regulatory framework for data protection in both the government and the private sector, creating and empowering the National Privacy Commission (NPC) to enforce such a law.
Therefore, any organization processing personal data must prioritize understanding and adhering to NPC compliance requirements.
- Understanding the National Privacy Commission (NPC)
- Compliance Timeline of the Data Privacy Act of 2012
- How to Incorporate Data Privacy Compliance in Business Operations
- What are the Risks and Penalties for Non-Compliance
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding the National Privacy Commission (NPC)
The National Privacy Commission (NPC) operates as an independent regulatory body mandated to implement and enforce the Data Privacy Act of 2012 (DPA), its Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR), and relevant public issuances. Its primary mandate is to safeguard the fundamental human right to privacy while simultaneously ensuring the free flow of information to foster innovation and economic growth.
Adherence to NPC regulations is a strict requirement for any legal entity or individual engaged in processing personal data within or outside the Philippines, subject to extraterritorial application. Such compliance is critical not only for avoiding or at least mitigating the risk of substantial financial penalties and legal liabilities but also for demonstrating a commitment to customer welfare, strengthening brand reputation, and establishing sustained trust.
Compliance Timeline of the Data Privacy Act of 2012
This timeline outlines the key requirements and deadlines for various compliance activities, including registration with the National Privacy Commission (NPC), personal data breach management, privacy impact assessments, and the exercise of data subject rights.
By adhering to these timelines, businesses can maintain transparency, accountability, and trust while avoiding penalties and ensuring the protection of personal data. Understanding these compliance milestones is essential for fostering a culture of privacy and safeguarding personally identifiable information in today’s data-driven world.
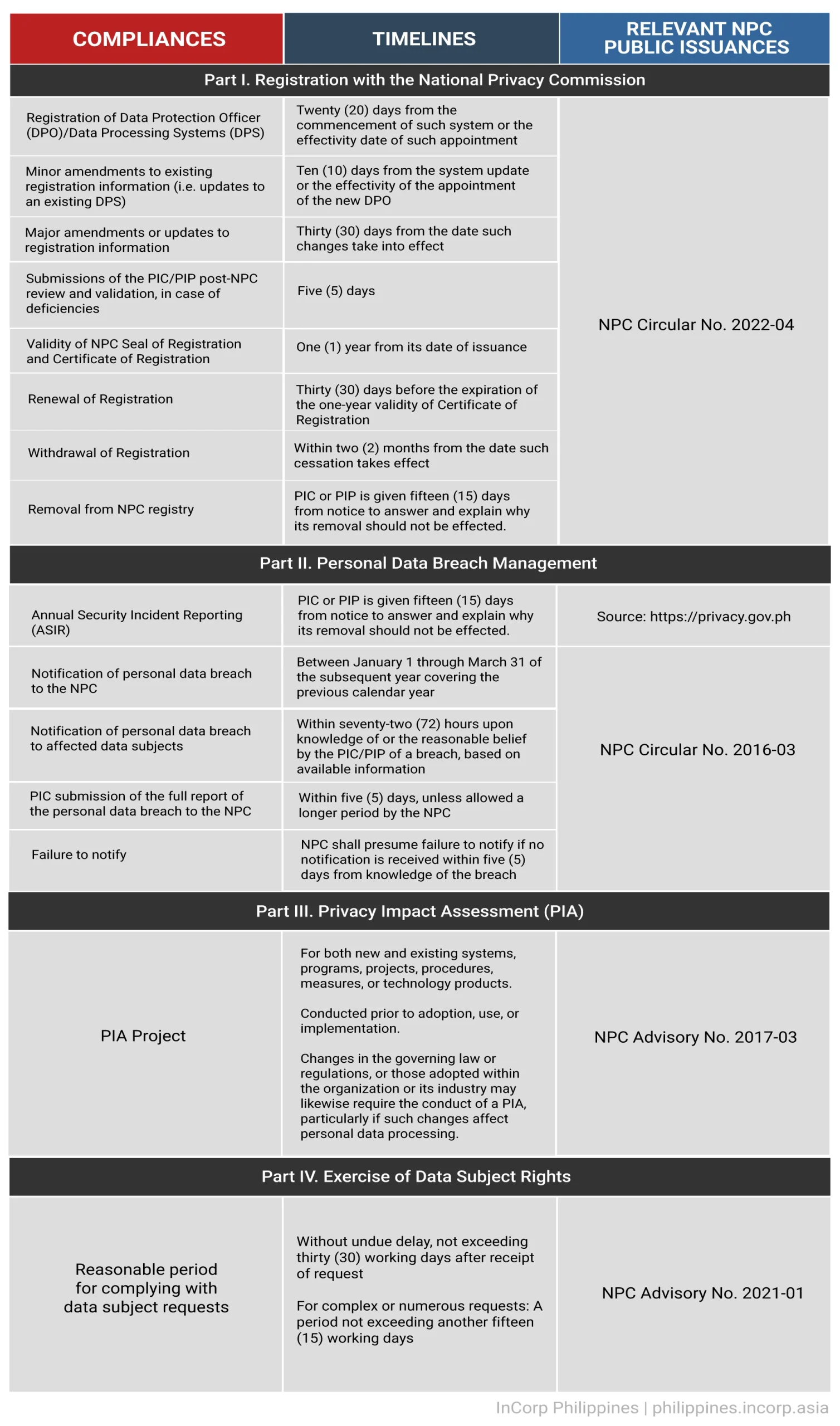
Staying proactive and informed about these compliance requirements, including ASIR, will enable businesses to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape effectively, ensuring sustainable business operations and risk management in an increasingly privacy-conscious environment.
How to Incorporate Data Privacy Compliance in Business Operations
Incorporating data privacy compliance into your business processes is essential for protecting personal data, maintaining customer trust, and adhering to legal requirements. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you integrate data privacy compliance effectively:
- Understand Applicable Data Privacy Laws
- Identify the data privacy regulations relevant to your business (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, Philippine Data Privacy Act).
- Keep abreast of evolving updates in these regulations to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Conduct a Personal Data Inventory
- Assess what personal data your business collects, processes, and retains.
- Map out data flows to understand how information is handled across your organization.
- Develop a Data Privacy Policy
- Create a clear and comprehensive privacy policy outlining how data is collected, used, retained, shared, and protected.
- Ensure the policy is accessible to employees, customers, and stakeholders.
- Periodically review and make updates to the policy based on changes in applicable legislation, regulations, industry best practices, and internal company policies, procedures, and practices.
- Implement Data Protection Measures
- Use encryption, firewalls, and secure access controls to safeguard data.
- Regularly update software and systems to protect against vulnerabilities.
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022 is an international standard that focuses on best practices for information security controls (i.e. organizational, people, physical and technological controls) that your business may adopt.
- Train Employees on Data Privacy
- Educate your team on data privacy principles, regulations, and best practices.
- Conduct regular training sessions to reinforce compliance awareness.
- Integrate Privacy into Business Processes
- Apply the principle of “privacy by design” by embedding data protection measures into workflows, systems, and products from conceptualization, design, development and implementation.
- Minimize data collection to only what is necessary for business operations.
- Establish Consent and Transparency Practices
- Obtain clear and informed consent from individuals before collecting their data if consent is the sole legal basis for personal data processing.
- Be transparent about how data is used and provide options for individuals to manage their preferences.
- Communicate data privacy practices using a privacy notice upon data collection.
- Monitor Third-Party Compliance
- Ensure vendors and partners handling your data comply with privacy regulations.
- Include data protection clauses in contracts with third parties.
- Create a Data Breach Response Plan
- Develop a clear protocol for identifying, escalating, assessing, reporting, and mitigating personal data breaches.
- Notify affected individuals and the NPC within 72 hours upon knowledge of or reasonable belief that a breach has occurred, as required by law.
- Regularly Review and Update Practices
- Conduct periodic reviews of your data privacy practices to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Stay proactive in adapting to new regulations and emerging threats.
By embedding these steps into your business processes, you can ensure robust data privacy compliance while fostering trust and confidence among your customers and stakeholders.
What are the Risks of Non-Compliance
Failure to adhere to data privacy regulations exposes organizations to severe consequences that extend far beyond simple regulatory oversight.
- Financial Penalties: The NPC can impose fines ranging from PHP 100,000 to PHP 5 million.
- Administrative Fines: The total imposable fine for a single act of a PIC or a PIP, whether resulting in single or multiple infractions, shall not exceed PHP 5 million. For grave infractions, any natural person or juridical person shall be subject to administrative fines of 0.5% to 3% of the annual gross income of the immediately preceding year.
- Imprisonment: Certain violations can lead to civil, administrative, and criminal liabilities and imprisonment for responsible company officers who allowed the commission of the crime.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach can permanently damage your brand and customer loyalty.
- Business Disruption: Responding to an investigation or a data breach can drain resources and disrupt operations.
Penalties Under the DPA of 2012
Understanding the penalties under the Data Privacy Act (DPA) of 2012 is crucial for organizations handling personal data in the Philippines. Non-compliance with the law not only puts individuals’ privacy at risk but also exposes businesses to significant legal and financial consequences.
This section outlines the specific penalties and sanctions imposed for violations, emphasizing the importance of adhering to data privacy regulations.
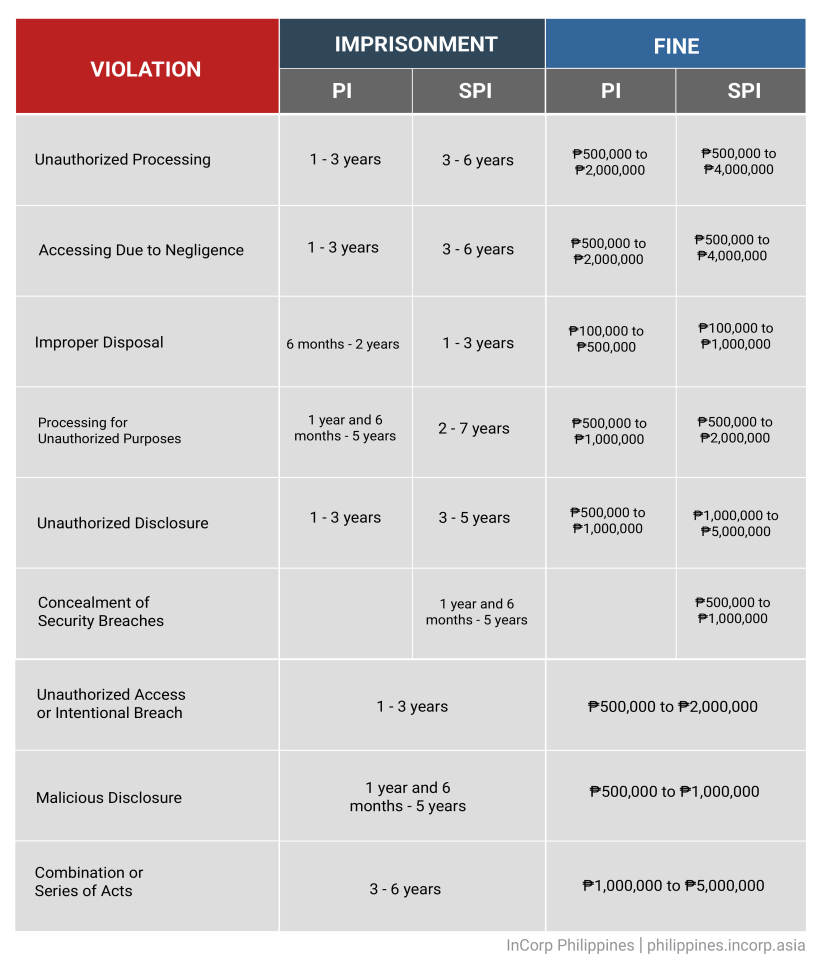
By understanding and avoiding these penalties, organizations can foster trust, enhance their reputation, and ensure sustainable operations in today’s data-driven world. Prioritizing data privacy is a proactive step toward building a secure and responsible business environment.
Ensure Your Organization Complies with NPC
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the National Privacy Commission (NPC) and why is it important for my business?
The NPC is the independent government body in the Philippines responsible for enforcing the Data Privacy Act (DPA) of 2012, its Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR) and relevant public issuances. If your organization collects and processes personal data, you are legally required to follow their regulations, subject to satisfying the criteria for NPC registration. Compliance is crucial for avoiding penalties and building trust with your customers.
Is NPC compliance mandatory for all businesses?
Your business may need to be registered with the NPC if it meets any, or a combination of, the following conditions:
- It employs two hundred fifty (250) or more persons;
- It processes sensitive personal information of one thousand (1,000) or more individuals;
- It processes data that will likely pose a risk to the rights and freedoms of data subjects.
However, exemption from NPC registration does not preclude the said regulator from performing compliance checks on the said organization.
How soon do I need to register my Data Protection Officer (DPO)?
You must register your DPO with the NPC within twenty (20) days of their appointment. The same timeline applies to the registration of new Data Processing Systems (DPS).
What are the first steps to making my business compliant?
Start by conducting a personal data inventory to understand what personal data you collect, how it flows through your organization, and where it is stored. Use this information to develop a clear privacy policy and train your employees in it.
What happens if my organization does not comply with the Data Privacy Act?
Non-compliance can result in hefty fines (PHP 100,000 to PHP 5 million), possible jail time for responsible officers, serious harm to your brand, and costly business disruptions.


